

Now when you have the variances you use the formula for Z-test two independent samples or you can use the calculator provided. Standard deviations for each sample thus you need to take the square of the standar deviations to find the variances:
Hypothesis test calculator ztest how to#
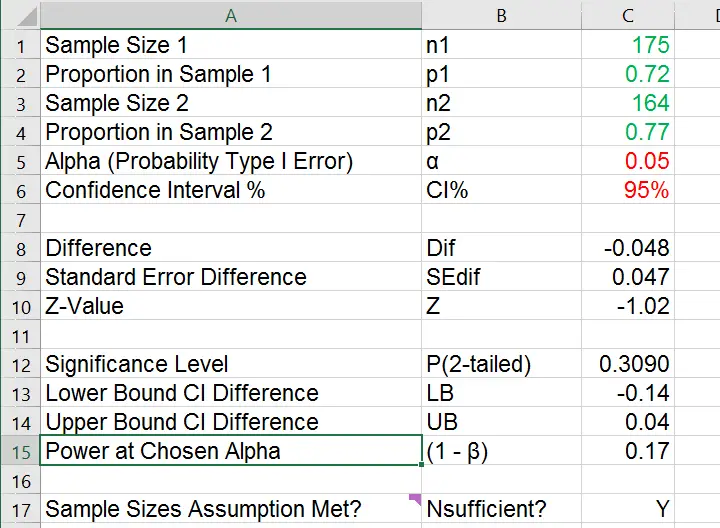
You will find a description of how to conduct a two sample t-test below the calculator. If you dont know them, provide some data about your sample(s): sample size, mean, and standard deviation, and our t-test calculator will compute the t-score and. Enter your sample means, sample standard deviations, sample sizes, hypothesized difference in means, test type, and significance level to calculate your results. This t-test calculator allows you to use either the p-value approach or the critical regions approach to hypothesis testing Enter your t-score, and the number of degrees of freedom. When performing a Z-test on two independent samples you want to sum the variances of the means and then take the square root to find the standard deviation of variance sum. Use the calculator below to analyze the results of a difference in sample means hypothesis test. It is the method to determine whether two sample means are approximately the same or different when their variance is known and the sample size is large (should be > 30). The soils appear to differ with respect to average shear strength, at the 1% significance level? Z-test is a statistical method to determine whether the distribution of the test statistics can be approximated by a normal distribution. For a claim to be a testable null hypothesis, it must specify a value for some population parameter that can form the basis for assuming a sampling distribution for a test statistic. P-value formula, Z-score formula, T-statistic. Null hypothesis: is the claim being assessed in a hypothesis. Powerful p-value calculator online: calculate statistical significance using a Z-test or T-test statistic. Sample means when you want to see if there is any different between the means of two normally distributed samples.Įxample, Shear strength measurements derived from unconfined compression tests for two types of soils gave the results shown in the following table (measurements in tons per square foot). Null hypothesis, Alternative hypothesis, P value and Z test. This handout will take you through one of the examples we. When do you use Z-test two independent sample means?Ī Z-test assumes the data is normally distributed which according to the central limit theorem is when the sample size is large, usually when n > 30. The 1-proportion z test is used to test hypotheses regarding population proportions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
